Note
Click here to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder
Using scikit-learn FedAvg on IRIS dataset¶
This example illustrate an advanced usage of SubstraFL as it does not use the SubstraFL PyTorch interface, but showcases the general SubstraFL interface that you can use with any ML framework.
This example is based on:
Dataset: IRIS, tabular dataset to classify iris type
Model type: Logistic regression using Scikit-Learn
FL setup: three organizations, two data providers and one algo provider
This example does not use the deployed platform of Substra, it runs in local mode.
To run this example, you have two options:
Recommended option: use a hosted Jupyter notebook. With this option you don’t have to install anything, just run the notebook. To access the hosted notebook, scroll down at the bottom of this page and click on the Launch Binder button.
Run the example locally. To do that you need to download and unzip the assets needed to run it in the same directory as used this example.
Please ensure to have all the libraries installed. A requirements.txt file is included in the zip file, where you can run the command
pip install -r requirements.txtto install them.Substra and SubstraFL should already be installed. If not follow the instructions described here: Installation.
Setup¶
We work with three different organizations. Two organizations provide a dataset, and a third one provides the algorithm and registers the machine learning tasks.
This example runs in local mode, simulating a federated learning experiment.
In the following code cell, we define the different organizations needed for our FL experiment.
import numpy as np
from substra import Client
SEED = 42
np.random.seed(SEED)
# Choose the subprocess mode to locally simulate the FL process
N_CLIENTS = 3
clients_list = [Client(backend_type="subprocess") for _ in range(N_CLIENTS)]
clients = {client.organization_info().organization_id: client for client in clients_list}
# Store organization IDs
ORGS_ID = list(clients)
ALGO_ORG_ID = ORGS_ID[0] # Algo provider is defined as the first organization.
DATA_PROVIDER_ORGS_ID = ORGS_ID[1:] # Data provider orgs are the last two organizations.
Data and metrics¶
Data preparation¶
This section downloads (if needed) the IRIS dataset using the Scikit-Learn dataset module. It extracts the data locally create two folders: one for each organization.
Each organization will have access to half the train data, and to half the test data.
import pathlib
from sklearn_fedavg_assets.dataset.iris_dataset import setup_iris
# Create the temporary directory for generated data
(pathlib.Path.cwd() / "tmp").mkdir(exist_ok=True)
data_path = pathlib.Path.cwd() / "tmp" / "data_iris"
setup_iris(data_path=data_path, n_client=len(DATA_PROVIDER_ORGS_ID))
Dataset registration¶
from substra.sdk.schemas import DatasetSpec
from substra.sdk.schemas import Permissions
from substra.sdk.schemas import DataSampleSpec
assets_directory = pathlib.Path.cwd() / "sklearn_fedavg_assets"
permissions_dataset = Permissions(public=False, authorized_ids=[ALGO_ORG_ID])
dataset = DatasetSpec(
name="Iris",
type="npy",
data_opener=assets_directory / "dataset" / "iris_opener.py",
description=assets_directory / "dataset" / "description.md",
permissions=permissions_dataset,
logs_permission=permissions_dataset,
)
dataset_keys = {}
train_datasample_keys = {}
test_datasample_keys = {}
for i, org_id in enumerate(DATA_PROVIDER_ORGS_ID):
client = clients[org_id]
# Add the dataset to the client to provide access to the opener in each organization.
dataset_keys[org_id] = client.add_dataset(dataset)
assert dataset_keys[org_id], "Missing data manager key"
client = clients[org_id]
# Add the training data on each organization.
data_sample = DataSampleSpec(
data_manager_keys=[dataset_keys[org_id]],
path=data_path / f"org_{i+1}" / "train",
)
train_datasample_keys[org_id] = client.add_data_sample(
data_sample,
local=True,
)
# Add the testing data on each organization.
data_sample = DataSampleSpec(
data_manager_keys=[dataset_keys[org_id]],
path=data_path / f"org_{i+1}" / "test",
)
test_datasample_keys[org_id] = client.add_data_sample(
data_sample,
local=True,
)
Metrics registration¶
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
import numpy as np
from substrafl.remote.register import add_metric
from substrafl.dependency import Dependency
metric_deps = Dependency(pypi_dependencies=["numpy==1.23.1", "scikit-learn==1.1.1"])
permissions_metric = Permissions(public=False, authorized_ids=[ALGO_ORG_ID] + DATA_PROVIDER_ORGS_ID)
def accuracy(datasamples, predictions_path):
y_true = datasamples["targets"]
y_pred = np.load(predictions_path)
return accuracy_score(y_true, y_pred)
metric_key = add_metric(
client=clients[ALGO_ORG_ID],
metric_function=accuracy,
permissions=permissions_metric,
dependencies=metric_deps,
)
Specify the machine learning components¶
SubstraFL can be used with any machine learning framework. The framework dependent functions are written in the Algorithm object.
In this section, you will:
register a model and its dependencies
write your own Sklearn SubstraFL algorithm
specify the federated learning strategy
specify the organizations where to train and where to aggregate
specify the organizations where to test the models
actually run the computations
Model definition¶
The machine learning model used here is a logistic regression. The warm_start argument is essential in this example as it indicates to use the current state of the model as initialization for the future training. By default scikit-learn uses max_iter=100, which means the model trains on up to 100 epochs. When doing federated learning, we don’t want to train too much locally at every round otherwise the local training will erase what was learned from the other centers. That is why we set max_iter=3.
import os
from sklearn import linear_model
cls = linear_model.LogisticRegression(random_state=SEED, warm_start=True, max_iter=3)
# Optional:
# Scikit-Learn raises warnings in case of non convergence, that we choose to disable here.
# As this example runs with python subprocess, the way to disable it is to use following environment
# variable:
os.environ["PYTHONWARNINGS"] = "ignore:lbfgs failed to converge (status=1):UserWarning"
SubstraFL algo definition¶
This section is the most important one for this example. We will define here the function that will run locally on each node to train the model.
As SubstraFL does not provide an algorithm comptatible with Sklearn, we need to define one using the provided documentation on Base Class.
To define a custom algorithm, we will need to inherit from the base class Algo, and to define two properties and four methods:
strategies (property): the list of strategies our algorithm is compatible with.
model (property): a property that returns the model from the defined algo.
train (method): a function to describe the training process to apply to train our model in a federated way. The train method must accept as parameters datasamples and shared_state.
predict (method): a function to describe how to compute the predictions from the algo model. The predict method must accept as parameters datasamples, shared_state and predictions_path.
save (method): specify how to save the important states of our algo.
load (method): specify how to load the important states of our algo from a previously saved filed by the save function describe above.
from substrafl import algorithms
from substrafl import remote
from substrafl import schemas as fl_schemas
import joblib
from typing import Optional
import shutil
# The Iris dataset proposes four attributes to predict three different classes.
INPUT_SIZE = 4
OUTPUT_SIZE = 3
class SklearnLogisticRegression(algorithms.Algo):
def __init__(self, model, seed=None):
super().__init__(model=model, seed=seed)
self._model = model
# We need all different instances of the algorithm to have the same
# initialization.
self._model.coef_ = np.ones((OUTPUT_SIZE, INPUT_SIZE))
self._model.intercept_ = np.zeros(3)
self._model.classes_ = np.array([-1])
if seed is not None:
np.random.seed(seed)
@property
def strategies(self):
"""List of compatible strategies"""
return [fl_schemas.StrategyName.FEDERATED_AVERAGING]
@property
def model(self):
return self._model
@remote.remote_data
def train(
self,
datasamples,
shared_state: Optional[fl_schemas.FedAvgAveragedState] = None,
) -> fl_schemas.FedAvgSharedState:
"""The train function to be executed on organizations containing
data we want to train our model on. The @remote_data decorator is mandatory
to allow this function to be sent and executed on the right organization.
Args:
datasamples: datasamples extracted from the organizations data using
the given opener.
shared_state (Optional[fl_schemas.FedAvgAveragedState], optional):
shared_state provided by the aggregator. Defaults to None.
Returns:
fl_schemas.FedAvgSharedState: State to be sent to the aggregator.
"""
if shared_state is not None:
# If we have a shared state, we update the model parameters with
# the average parameters updates.
self._model.coef_ += np.reshape(
shared_state.avg_parameters_update[:-1],
(OUTPUT_SIZE, INPUT_SIZE),
)
self._model.intercept_ += shared_state.avg_parameters_update[-1]
# To be able to compute the delta between the parameters before and after training,
# we need to save them in a temporary variable.
old_coef = self._model.coef_
old_intercept = self._model.intercept_
# Model training.
self._model.fit(datasamples["data"], datasamples["targets"])
# We compute de delta.
delta_coef = self._model.coef_ - old_coef
delta_bias = self._model.intercept_ - old_intercept
# We reset the model parameters to their state before training in order to remove
# the local updates from it.
self._model.coef_ = old_coef
self._model.intercept_ = old_intercept
# We output the length of the dataset to apply a weighted average between
# the organizations regarding their number of samples, and the local
# parameters updates.
# These updates are sent to the aggregator to compute the average
# parameters updates, that we will receive in the next round in the
# `shared_state`.
return fl_schemas.FedAvgSharedState(
n_samples=len(datasamples["targets"]),
parameters_update=[p for p in delta_coef] + [delta_bias],
)
@remote.remote_data
def predict(self, datasamples, shared_state, predictions_path):
"""The predict function to be executed on organizations containing
data we want to test our model on. The @remote_data decorator is mandatory
to allow this function to be sent and executed on the right organization.
Args:
datasamples: datasamples extracted from the organizations data using
the given opener.
shared_state: shared_state provided by the aggregator.
predictions_path: Path where to save the predictions.
This path is provided by Substra and the metric will automatically
get access to this path to load the predictions.
"""
predictions = self._model.predict(datasamples["data"])
if predictions_path is not None:
np.save(predictions_path, predictions)
# np.save() automatically adds a ".npy" to the end of the file.
# We rename the file produced by removing the ".npy" suffix, to make sure that
# predictions_path is the actual file name.
shutil.move(str(predictions_path) + ".npy", predictions_path)
def save(self, path):
joblib.dump(
{
"model": self._model,
"coef": self._model.coef_,
"bias": self._model.intercept_,
},
path,
)
def load(self, path):
loaded_dict = joblib.load(path)
self._model = loaded_dict["model"]
self._model.coef_ = loaded_dict["coef"]
self._model.intercept_ = loaded_dict["bias"]
return self
Federated Learning strategies¶
from substrafl.strategies import FedAvg
strategy = FedAvg(algo=SklearnLogisticRegression(model=cls, seed=SEED))
Where to train where to aggregate¶
from substrafl.nodes import TrainDataNode
from substrafl.nodes import AggregationNode
aggregation_node = AggregationNode(ALGO_ORG_ID)
# Create the Train Data Nodes (or training tasks) and save them in a list
train_data_nodes = [
TrainDataNode(
organization_id=org_id,
data_manager_key=dataset_keys[org_id],
data_sample_keys=[train_datasample_keys[org_id]],
)
for org_id in DATA_PROVIDER_ORGS_ID
]
Where and when to test¶
from substrafl.nodes import TestDataNode
from substrafl.evaluation_strategy import EvaluationStrategy
# Create the Test Data Nodes (or testing tasks) and save them in a list
test_data_nodes = [
TestDataNode(
organization_id=org_id,
data_manager_key=dataset_keys[org_id],
test_data_sample_keys=[test_datasample_keys[org_id]],
metric_keys=[metric_key],
)
for org_id in DATA_PROVIDER_ORGS_ID
]
my_eval_strategy = EvaluationStrategy(test_data_nodes=test_data_nodes, eval_frequency=1)
Running the experiment¶
from substrafl.experiment import execute_experiment
# Number of times to apply the compute plan.
NUM_ROUNDS = 6
algo_deps = Dependency(pypi_dependencies=["numpy==1.23.1", "torch==1.11.0"])
compute_plan = execute_experiment(
client=clients[ALGO_ORG_ID],
strategy=strategy,
train_data_nodes=train_data_nodes,
evaluation_strategy=my_eval_strategy,
aggregation_node=aggregation_node,
num_rounds=NUM_ROUNDS,
experiment_folder=str(pathlib.Path.cwd() / "tmp" / "experiment_summaries"),
dependencies=algo_deps,
)
Out:
Compute plan progress: 0%| | 0/50 [00:00<?, ?it/s]/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/owkin-substra-documentation/checkouts/0.26.3/docs/src/substra/substra/sdk/backends/local/backend.py:580: UserWarning: `transient=True` is ignored in local mode
warnings.warn("`transient=True` is ignored in local mode")
Compute plan progress: 2%|2 | 1/50 [00:00<00:42, 1.14it/s]
Compute plan progress: 4%|4 | 2/50 [00:01<00:42, 1.13it/s]
Compute plan progress: 6%|6 | 3/50 [00:02<00:41, 1.13it/s]
Compute plan progress: 8%|8 | 4/50 [00:03<00:40, 1.13it/s]
Compute plan progress: 10%|# | 5/50 [00:04<00:39, 1.13it/s]
Compute plan progress: 12%|#2 | 6/50 [00:05<00:38, 1.13it/s]
Compute plan progress: 14%|#4 | 7/50 [00:06<00:37, 1.14it/s]
Compute plan progress: 16%|#6 | 8/50 [00:07<00:36, 1.15it/s]
Compute plan progress: 18%|#8 | 9/50 [00:07<00:35, 1.15it/s]
Compute plan progress: 20%|## | 10/50 [00:08<00:34, 1.15it/s]
Compute plan progress: 22%|##2 | 11/50 [00:09<00:33, 1.15it/s]
Compute plan progress: 24%|##4 | 12/50 [00:10<00:33, 1.15it/s]
Compute plan progress: 26%|##6 | 13/50 [00:11<00:32, 1.15it/s]
Compute plan progress: 28%|##8 | 14/50 [00:12<00:31, 1.14it/s]
Compute plan progress: 30%|### | 15/50 [00:13<00:30, 1.14it/s]
Compute plan progress: 32%|###2 | 16/50 [00:14<00:30, 1.13it/s]
Compute plan progress: 34%|###4 | 17/50 [00:14<00:28, 1.14it/s]
Compute plan progress: 36%|###6 | 18/50 [00:15<00:27, 1.15it/s]
Compute plan progress: 38%|###8 | 19/50 [00:16<00:27, 1.15it/s]
Compute plan progress: 40%|#### | 20/50 [00:17<00:26, 1.15it/s]
Compute plan progress: 42%|####2 | 21/50 [00:18<00:25, 1.15it/s]
Compute plan progress: 44%|####4 | 22/50 [00:19<00:24, 1.14it/s]
Compute plan progress: 46%|####6 | 23/50 [00:20<00:23, 1.14it/s]
Compute plan progress: 48%|####8 | 24/50 [00:21<00:22, 1.14it/s]
Compute plan progress: 50%|##### | 25/50 [00:21<00:21, 1.15it/s]
Compute plan progress: 52%|#####2 | 26/50 [00:22<00:20, 1.15it/s]
Compute plan progress: 54%|#####4 | 27/50 [00:23<00:20, 1.14it/s]
Compute plan progress: 56%|#####6 | 28/50 [00:24<00:19, 1.14it/s]
Compute plan progress: 58%|#####8 | 29/50 [00:25<00:18, 1.14it/s]
Compute plan progress: 60%|###### | 30/50 [00:26<00:17, 1.14it/s]
Compute plan progress: 62%|######2 | 31/50 [00:27<00:16, 1.15it/s]
Compute plan progress: 64%|######4 | 32/50 [00:27<00:15, 1.16it/s]
Compute plan progress: 66%|######6 | 33/50 [00:28<00:14, 1.15it/s]
Compute plan progress: 68%|######8 | 34/50 [00:29<00:13, 1.15it/s]
Compute plan progress: 70%|####### | 35/50 [00:30<00:13, 1.15it/s]
Compute plan progress: 72%|#######2 | 36/50 [00:31<00:12, 1.14it/s]
Compute plan progress: 74%|#######4 | 37/50 [00:32<00:11, 1.13it/s]
Compute plan progress: 76%|#######6 | 38/50 [00:33<00:10, 1.14it/s]
Compute plan progress: 78%|#######8 | 39/50 [00:34<00:09, 1.15it/s]
Compute plan progress: 80%|######## | 40/50 [00:34<00:08, 1.14it/s]
Compute plan progress: 82%|########2 | 41/50 [00:35<00:07, 1.14it/s]
Compute plan progress: 84%|########4 | 42/50 [00:36<00:06, 1.15it/s]
Compute plan progress: 86%|########6 | 43/50 [00:37<00:06, 1.14it/s]
Compute plan progress: 88%|########8 | 44/50 [00:38<00:05, 1.14it/s]
Compute plan progress: 90%|######### | 45/50 [00:39<00:04, 1.15it/s]
Compute plan progress: 92%|#########2| 46/50 [00:40<00:03, 1.16it/s]
Compute plan progress: 94%|#########3| 47/50 [00:41<00:02, 1.16it/s]
Compute plan progress: 96%|#########6| 48/50 [00:41<00:01, 1.15it/s]
Compute plan progress: 98%|#########8| 49/50 [00:42<00:00, 1.16it/s]
Compute plan progress: 100%|##########| 50/50 [00:43<00:00, 1.16it/s]
Compute plan progress: 100%|##########| 50/50 [00:43<00:00, 1.15it/s]
Explore the results¶
Listing results¶
import pandas as pd
performances_df = pd.DataFrame(client.get_performances(compute_plan.key).dict())
print("\nPerformance Table: \n")
print(performances_df[["worker", "round_idx", "performance"]])
Out:
Performance Table:
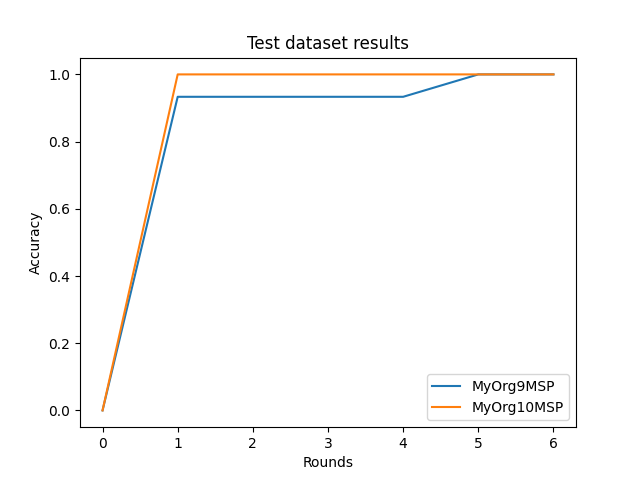
worker round_idx performance
0 MyOrg9MSP 0 0.000000
1 MyOrg10MSP 0 0.000000
2 MyOrg9MSP 1 0.933333
3 MyOrg10MSP 1 1.000000
4 MyOrg9MSP 2 0.933333
5 MyOrg10MSP 2 1.000000
6 MyOrg9MSP 3 0.933333
7 MyOrg10MSP 3 1.000000
8 MyOrg9MSP 4 0.933333
9 MyOrg10MSP 4 1.000000
10 MyOrg9MSP 5 1.000000
11 MyOrg10MSP 5 1.000000
12 MyOrg9MSP 6 1.000000
13 MyOrg10MSP 6 1.000000
Plot results¶
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.title("Test dataset results")
plt.xlabel("Rounds")
plt.ylabel("Accuracy")
for org_id in DATA_PROVIDER_ORGS_ID:
df = performances_df[performances_df["worker"] == org_id]
plt.plot(df["round_idx"], df["performance"], label=org_id)
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.show()
Download a model¶
from substrafl.model_loading import download_algo_files
from substrafl.model_loading import load_algo
client_to_dowload_from = DATA_PROVIDER_ORGS_ID[0]
round_idx = None
algo_files_folder = str(pathlib.Path.cwd() / "tmp" / "algo_files")
download_algo_files(
client=clients[client_to_dowload_from],
compute_plan_key=compute_plan.key,
round_idx=round_idx,
dest_folder=algo_files_folder,
)
cls = load_algo(input_folder=algo_files_folder).model
print("Coefs: ", cls.coef_)
print("Intercepts: ", cls.intercept_)
Out:
Coefs: [[ 1.16237637 1.80062789 -0.59844895 0.16076327]
[ 1.02009926 0.51773141 1.04883079 0.61084198]
[ 0.26141703 0.12553336 1.99351081 1.67228741]]
Intercepts: [ 0.21601049 0.1066958 -0.32270629]
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 43.907 seconds)